[Vue][Chapter8] vuex
1. 설치
-
npm으로 설치
npm install vuex --save -
promise 설치
npm install es6-promise --save # NPM
2. 상태관리패턴.
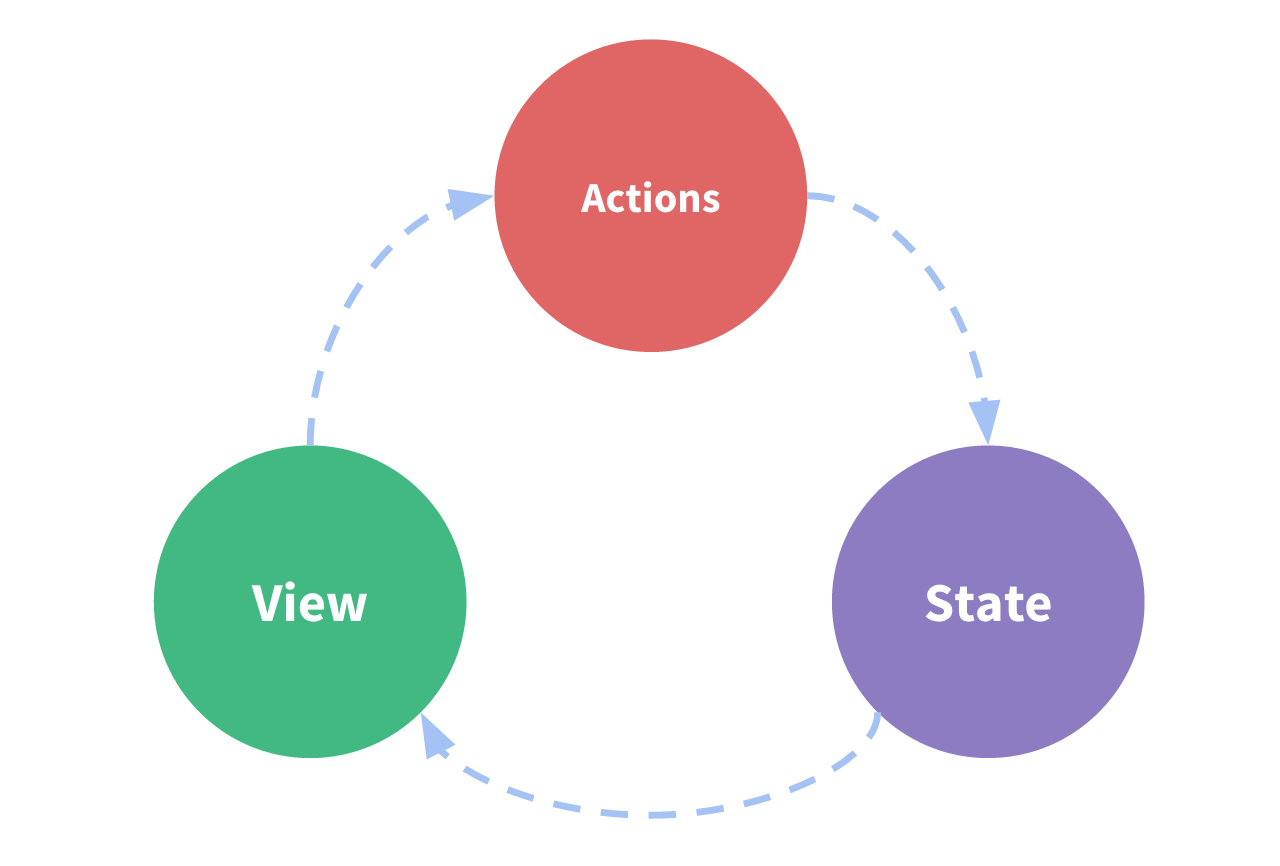
- Vuex는 Vue.js앱에 대한 상태관리 패턴+ 라이브러리
- 상태는 앱을 작동하는 원본 소스.(=data)
- 뷰는 상태의 선언적 매핑(=template)
- 액션은 뷰 에서 사용자 입력에 대해 반응적으로 상태를 바꾸는 방법.(=method)
new Vue({
// 상태
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// 뷰
template: `
<div> {{ count }}</div>
`,
// 액션
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
})
2.1 기존 방식의 문제점
- 공통의 상태를 공유하는 여러 컴포넌트가 있는 경우 단순함이 떨어짐.
- 여러 뷰는 같은 상태에 의존 -> 유지보수 힘듬
- 서로 다른 뷰의 작업은 동일한 상태를 반영해야 할 수 있음.
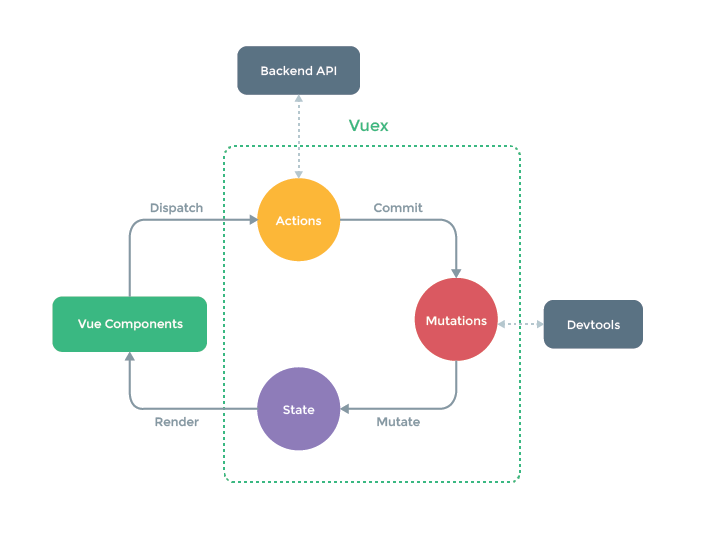
- method : 동기 ,비동기
- action : 비동기
- mutations : state 변경
- state : data 영역
- Vue Components : DOM영역
3. 핵심 개념
3.1 State(상태)
- 단일 상태 트리를 사용
- 모든 어플리케이션 수준의 상태를 포함하여, 원본 소스역할을 함.
- 각 App마다 하나의 저장소만 가짐
- 특정 상태를 쉽게 찾을수 있음.
- 모듈성과 충돌하지않음.
3.2 Getters
- Vue Instance의 Computed와 같은 역할. (computed)
- State를 기반으로 계산
- component가 vuex의 state를 직접 접근하는 코드가 중복될때, Store의 state를 참조하는 Getters 사용(캐싱)
-
정의
getters:{ // 첫번째 파라미터는 항상 state이어야함. countMsg(state){ state.count +=1; } } -
사용
this.$store.getters.countMsg; - mapGetters
-
다수의 getters를 좀 더 간단히 호출
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default { // ... computed: { // mix the getters into computed with object spread operator ...mapGetters([ 'doneTodosCount', 'anotherGetter', // ... ]) } }
-
3.3 Mutations
- State의 상태를 변경하는 유일한 방법(동기)
- State의 값의 추적을 위해 동기적 기능에 사용함.
- 직접 호출이 불가능하고, store.commit(‘이름’)으로 호출.
-
정의
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 1 }, mutations: { increment (state,num) { // mutate state state.count+=num; } } }) -
호출
// 첫번째인자 : mutations에있는 함수 명, ... store.commit('increment', 33); -
mapMutaions(여러 Mutation 처리)
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' export default { // ... methods: { ...mapMutations([ 'increment', // map `this.increment()` to `this.$store.commit('increment')` // `mapMutations` also supports payloads: 'incrementBy' // map `this.incrementBy(amount)` to `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)` ]), ...mapMutations({ add: 'increment' // map `this.add()` to `this.$store.commit('increment')` }) } } // 호출 store.commit('increment');
3.4 Actions
- 상태를 변이 시키는 대신에 액션으로 변이에 대한 commit 처리 (비동기)
- Actions는 비동기 로직의 처리가 종료되면 Mutaions를 호출(동기)
- 동기, 비동기를 구분하자는 취지(Mutations : 동기, Actions: 비동기)
-
정의
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { // 첫번째 매개인자는 무조건 context이어야함(mutation를 가리킴) increment (context) { context.commit('increment') } } }) -
호출
// dispatch with a payload store.dispatch('incrementAsync', { amount: 10 }) // dispatch with an object store.dispatch({ type: 'incrementAsync', amount: 10 }) -
mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { // ... methods: { ...mapActions([ 'increment', // map `this.increment()` to `this.$store.dispatch('increment')` // `mapActions` also supports payloads: 'incrementBy' // map `this.incrementBy(amount)` to `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)` ]), ...mapActions({ add: 'increment' // map `this.add()` to `this.$store.dispatch('increment')` }) } }